0002 - Add Two Numbers
problem
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The digits are stored in reverse order, and each of their nodes contains a single digit. Add the two numbers and return the sum as a linked list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
Example 1:
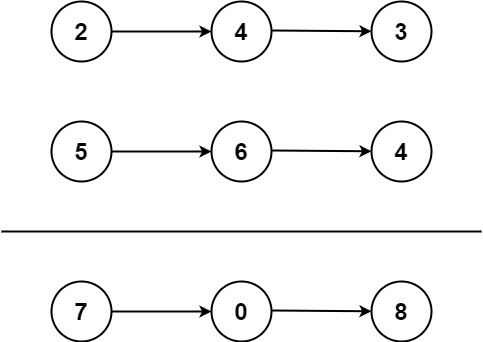
Input: l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4] Output: [7,0,8] Explanation: 342 + 465 = 807.
Example 2:
Input: l1 = [0], l2 = [0] Output: [0]
Example 3:
Input: l1 = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9], l2 = [9,9,9,9] Output: [8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in each linked list is in the range
[1, 100]. 0 <= Node.val <= 9- It is guaranteed that the list represents a number that does not have leading zeros.
submission
// Definition for singly-linked list.
// #[derive(PartialEq, Eq, Clone, Debug)]
// pub struct ListNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub next: Option<Box<ListNode>>
// }
//
// impl ListNode {
// #[inline]
// fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// ListNode {
// next: None,
// val
// }
// }
// }
impl Solution {
pub fn add_two_numbers(
mut l1: Option<Box<ListNode>>,
mut l2: Option<Box<ListNode>>,
) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> {
let mut carry = 0i32;
// this is the core trick of this solution
// curr actually point to the tail of added result
// so we could keep appending new digit to it
// without dummy node and unwrap operations
let mut head: Option<Box<ListNode>> = None;
let mut curr = &mut head;
while l1.is_some() || l2.is_some() || carry != 0 {
// unify our logic for any situation
carry += l1.as_ref().map_or(0, |n| n.val)
+ l2.as_ref().map_or(0, |n| n.val);
// append new digit
let sum_node =
curr.insert(Box::new(ListNode::new(carry % 10)));
// update curr
curr = &mut sum_node.next;
carry /= 10;
// update l1 & l2
l1 = l1.and_then(|n| n.next);
l2 = l2.and_then(|n| n.next);
}
head
}
}