0011 - Container With Most Water
problem
You are given an integer array height of length n. There are n vertical lines drawn such that the two endpoints of the ith line are (i, 0) and (i, height[i]).
Find two lines that together with the x-axis form a container, such that the container contains the most water.
Return the maximum amount of water a container can store.
Notice that you may not slant the container.
Example 1:
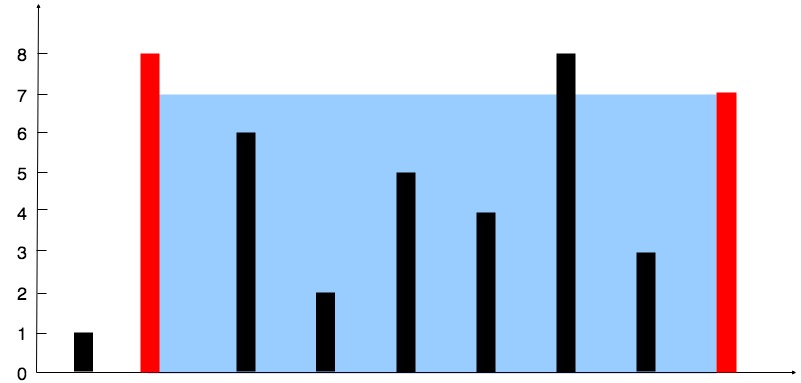
Input: height = [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7] Output: 49 Explanation: The above vertical lines are represented by array [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]. In this case, the max area of water (blue section) the container can contain is 49.
Example 2:
Input: height = [1,1] Output: 1
Constraints:
n == height.length2 <= n <= 1050 <= height[i] <= 104
submission
impl Solution {
// area = W x H, if we start at the leftmost and rightmost lines,
// and keep shrinking W = (R - L) until it becomes 0, the area can
// only increase if H increase, since H = min(H[l], H[r]), we must
// always choose the shorter side to shrink at each step.
// When H[l] == H[r], choose either side is OK, because if there
// is a larger rectangle between l and r, it must have two side
// l' and r' satisifing l < l' && H[l'] > H[l] and
// r' < r && H[r'] > H[r], meaning eventually we have to move
// both sides, so we can't miss it with these steps.
// By following these steps, we are searching for the maxium area
// within the leftmost and rightmost lines with the best strategy
// we can possibly formulate.
pub fn max_area(height: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
let mut ans = 0;
// with Vec we get a DoubleEndedIterator
let mut iter = height.iter().enumerate();
let mut l = iter.next();
let mut r = iter.next_back();
while let (Some((i, h1)), Some((j, h2))) = (l, r) {
// record the maxium area
ans = ans.max(h1.min(h2) * (j - i) as i32);
// push inward on the shorter side
if h1 < h2 {
l = iter.next();
} else {
r = iter.next_back();
}
}
ans
}
}