3217 - Delete Nodes From Linked List Present in Array
problem
You are given an array of integers nums and the head of a linked list. Return the head of the modified linked list after removing all nodes from the linked list that have a value that exists in nums.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3], head = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: [4,5]
Explanation:
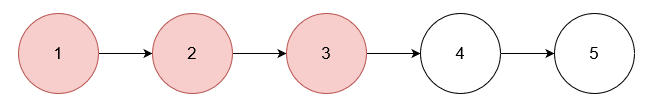
Remove the nodes with values 1, 2, and 3.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1], head = [1,2,1,2,1,2]
Output: [2,2,2]
Explanation:
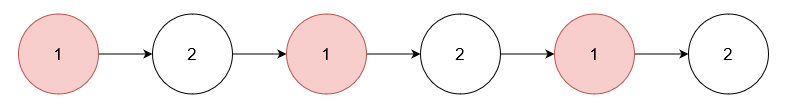
Remove the nodes with value 1.
Example 3:
Input: nums = [5], head = [1,2,3,4]
Output: [1,2,3,4]
Explanation:
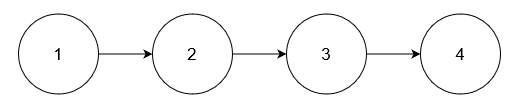
No node has value 5.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 1051 <= nums[i] <= 105- All elements in
numsare unique. - The number of nodes in the given list is in the range
[1, 105]. 1 <= Node.val <= 105- The input is generated such that there is at least one node in the linked list that has a value not present in
nums.
submission
// Definition for singly-linked list.
// #[derive(PartialEq, Eq, Clone, Debug)]
// pub struct ListNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub next: Option<Box<ListNode>>
// }
//
// impl ListNode {
// #[inline]
// fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// ListNode {
// next: None,
// val
// }
// }
// }
// rust solution focused on simplicity
use std::collections::HashSet;
impl Solution {
pub fn modified_list(
nums: Vec<i32>,
mut head: Option<Box<ListNode>>,
) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> {
let mut dummy = None;
let mut chain = &mut dummy;
let nums: HashSet<i32> = nums.into_iter().collect();
// take a node from the list
while let Some(mut node) = head.take() {
// use the next node as list head
head = node.next.take();
if !nums.contains(&node.val) {
// insert back if ...
chain = &mut chain.insert(node).next;
}
}
dummy
}
}